An impressive Regenerative Power
Our team of experts is committed to providing cryogenic processing and preservation services.
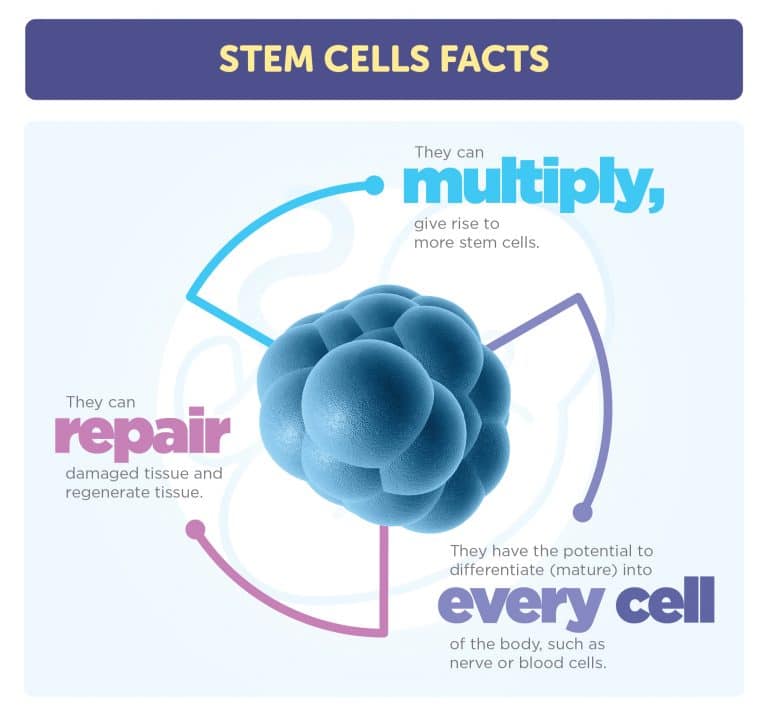
Stem Cells Facts
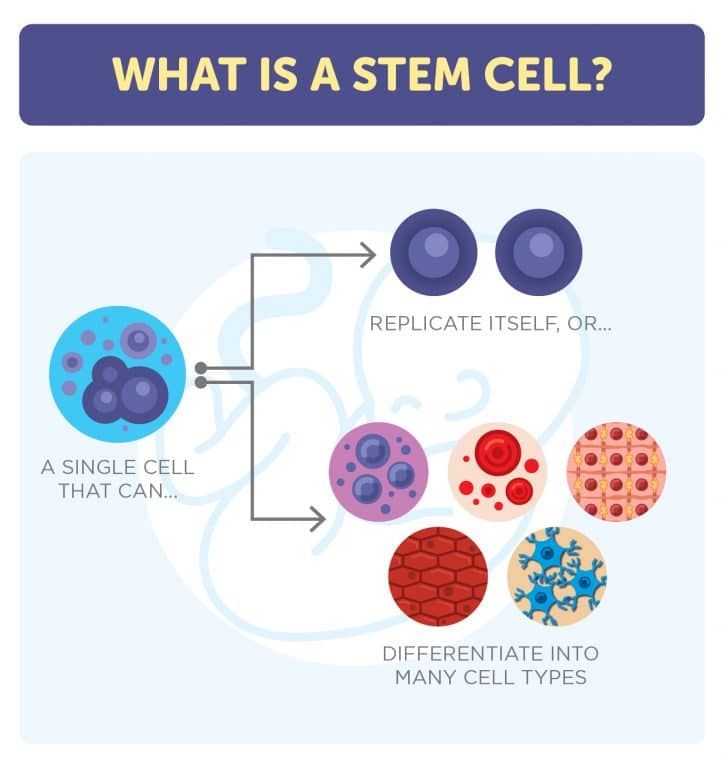
What are Stem Cells?
Have you wondered, “What are Stem Cells?”. Stem cells are the body’s “master cells.” They can divide (self-replicate), and they also have the potential to develop into many different cell types that make up the human body, such as organ tissue, blood, and the immune system. Stem cells also serve as a form of internal repair system, dividing and differentiating to replace damaged or dead tissue.
Why are Stem Cells Important?
Two biological characteristics make these cells unique and extremely valuable as a therapeutic; the ability to multiply and the capacity to develop into other types of cells. These two unique biological traits propel stem cells to the forefront of today’s scientific and medical community. Every day, cutting edge stem cell research furthers scientific understanding about how healthy cells develop and replace damaged cells.
In practice, this means that there is enormous potential for finding effective medical treatments and/or cures (never use the word cure, this can open up legal issues) for a wide array of diseases.
Stem cells are obtained from many sources, including embryos, afterbirth placenta, adult tissue, umbilical cord blood, adipose tissue, and dental pulp.
Why are Stem Cells Important?
Two biological characteristics make these cells unique and extremely valuable as a therapeutic; the ability to multiply and the capacity to develop into other types of cells. These two unique biological traits propel stem cells to the forefront of today’s scientific and medical community. Every day, cutting edge stem cell research furthers scientific understanding about how healthy cells develop and replace damaged cells.
In practice, this means that there is enormous potential for finding effective medical treatments and/or cures (never use the word cure, this can open up legal issues) for a wide array of diseases.
Stem cells are obtained from many sources, including embryos, afterbirth placenta, adult tissue, umbilical cord blood, adipose tissue, and dental pulp.
Types of Stem Cells
Stem cells are classified by their ability to differentiate into different cell types:
- Totipotent – a stem cell that can differentiate into all cell types. Examples include the first few cells after the division of the zygote.
- Pluripotent – a stem cell that can differentiate into almost all cell types. Examples include embryonic stem cells.
- Multipotent – a stem cell that can differentiate into a closely related family of cells. Examples include HSC and MSC.
- Oligopotent – a stem cell that can differentiate into a few cells. Examples include myeloid stem cells.
- Unipotent – a stem cell that can differentiate into only one cell type. Example muscle stem cells.